What
is an electronic load?
An electronic load is a test instrument designed to sink current and absorb power out of a power source. If a power supply is used to power a device, an electronic load is used to test the power supply by emulating the device under test (DUT).
An electronic load is a programmable
instrument that offers the user various modes of control such as constant voltage
(CV), constant current (CC), constant power (CP) or constant resistance (CR).
Who
uses electronic loads?
Device manufacturers and
design engineers use electronic loads to test numerous power devices such as
power supplies, DC-DC converters, chargers, adapters, batteries, solar panels,
fuel-cells, and more.
Why
do engineers use electronic loads instead of a fixed value power resistor?
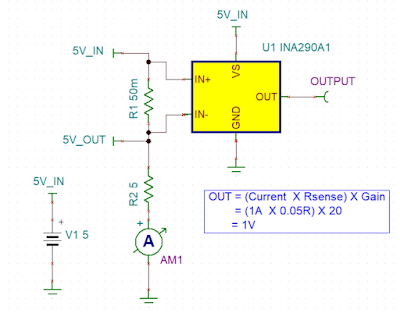
In situations where you need a purely resistive load and no closed loop control is required, it is sufficient to use a fixed value power resistor. A fixed value resistor presents many limitations. It is not adequate for loading and testing power sources that have complex testing requirements. Such tasks require sophisticated electronic load features to validate the various states of operation.
Constant
current operation mode
Constant current (CC) is the
most frequent mode in which an electronic load is used. In constant current
mode, the load will sink the programmed current independently from the output
voltage which is typically forced by the voltage source connected to it (for example
a battery).
Constant
voltage operation mode
In constant voltage (CV) mode
the electronic load sets a fixed programmable voltage across its terminals
independently from the input current. In CV mode, the current is set by the
current source connected to it – for example, a current charging circuit or a LED
current driver. The load adjusts its resistance dynamically to attain the
programmed voltage at any current established by the current source under test.
Constant
resistance operation
In constant resistance (CR)
mode, the load acts as a fixed programmable power resistor. An electronic
load’s CR mode is well-suited for loading a power source that is either a voltage
or current source. When the load connects to a voltage source it sinks a
current equal to the source potential divided by the programmed resistance
value.